Vacuum Moulding
This is a process that is used to manufacture a variety of products in thermoplastic materials. A mould,which is usedfor prducing the interior panels of lorry cabs, is attached to a platen (support plate)
The platen and mould are then lowered and rigid thermoplastic sheet material is clamped onto an air tight gasket and usually heated from above.One the thermoplastic sheet is softened enough then the air is blown in to raise the sheet in a slight bubble before the platen is raised bringing the mould into contact with plastic.Any air trapped between the platen and heated plastic sheet is then evacuated by a vacuum pump. Atmopheric pressure acting over the top surface completes the forming process by pressing the plastic sheet on to the mould. Once the plastic sheet has been cooled down below freezing pointthe air flow is reversed to lift the forming off the mould.
Line Bending
Blow Moulding
Compression Moulding
Injection Moulding
This is a process like Extrustion Moulding as the plastice pellets are put into a hopper that go to a heated barrel, while the mould is being clamped the machine.the heated up plastic is then injected in to the mould. Once mould is filled the cooling process begins and once mould is cooled down the mould is ejected and the process starts again.
Extrustion Moulding
This process can be compared to squeezing toothpaste from a tube.It is a continuous process used to produce both solid and hollow products that have a constant cross-section. E.g: Window Frames, Hose Pipe, Curtain Track, Garden Trellis. Thermoplastic granules are fed from a hopper by a rotating screw through a heated cylinder. The tapered shape of the screw compacts the plastic as it becomes plasticized.This part of the process is similar to the heating and compacting stages in the injection moulding process.The difference being that the softened materials material is allowed to flow out through a die in a continuous stream rather than be pumped intermittently in measured amounts into a mould.The die which is fitted to the end of the extruder barrel determines the cross-section of the extrusion.
Rotational Moulding

Rotational Moulding is a process used mainly to manufacture hollow shaped products such as footballs, road cones and storage tanks.
The machine has three arms which rotate about a fixed central point. Each arm stops in turn at one of three stations. Moulds are attached to end of each arm and are rotated continuously.The only time the moulds are not being rotated is when they are positioned at station 1 which is where the proess both begins and ends. At station 1 the mould is either being loaded with thermoplastic powder or the finished moulding is removed to start the process again. The cooling chamber is at station 3 and oven chamber is at station 2. The Temperture goes up to 230-400c whilst being rotated and the roational speed is between 2 and 20 r.p.m.
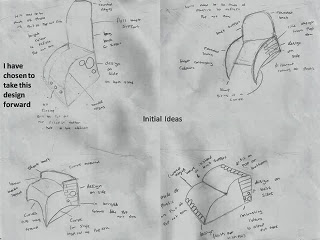
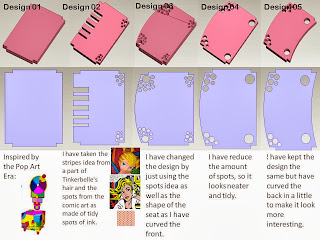
Jigs,Templates: these are imporant because they keep everything the same.